Traffic congestion: Tolls

One way to mitigate the consequences of drivers' selfish behavior, is by introducing tolls (or taxes) on certain parts of the road network. This is also known as road pricing.
A Santa Claus network

Poor Santa has to travel all across the country to deliver all his presents. How does he do this?
Layered networks I: From manufacturing plants to queueing networks
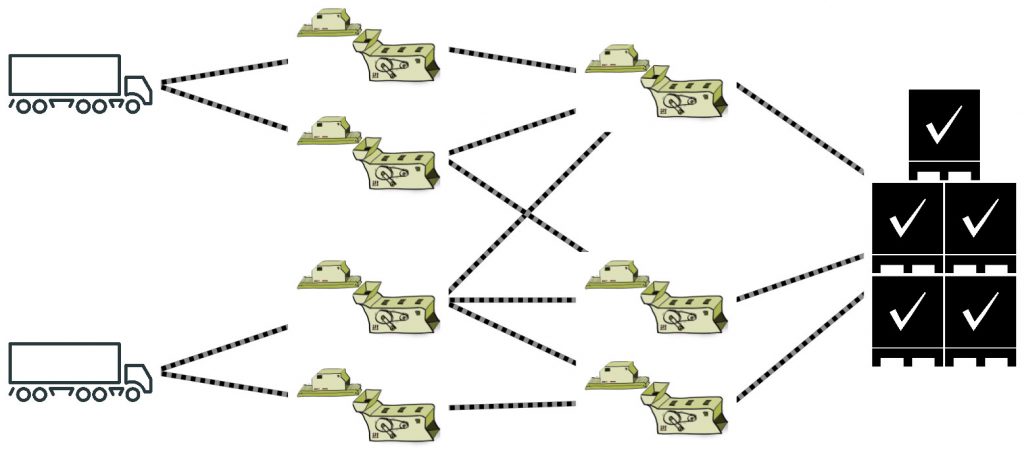
Manufacturing plants convert raw material into a final product. Think of cars, where the production line consists of a large number of phases to put all the different parts together into a working car. Big machines in such a plant perform the processing steps in different phases, which often have to be done in a specific order.
Traffic congestion: Pigou's example
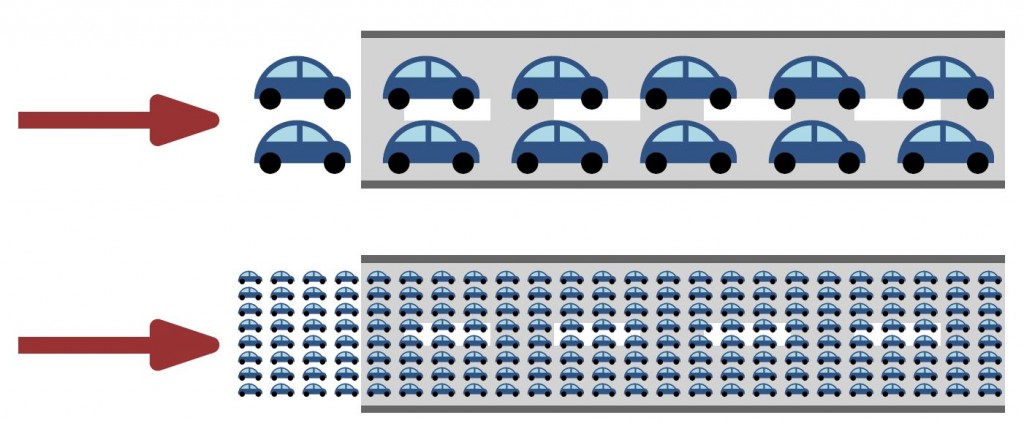
In network congestion models, we make some simplifying assumptions that make our life easier. In a large-scale system, each individual driver contributes a tiny amount to congestion, if we assume that every car controls the same amount of traffic.
Congested Roads

Traffic jams are one of the biggest inconveniences in modern time. They lead to stressful situations for commuters, and cause huge economical and environmental damage. How could mathematics help?
